Hello, you have come here looking for the meaning of the word
User:Algentem/sandbox3. In DICTIOUS you will not only get to know all the dictionary meanings for the word
User:Algentem/sandbox3, but we will also tell you about its etymology, its characteristics and you will know how to say
User:Algentem/sandbox3 in singular and plural. Everything you need to know about the word
User:Algentem/sandbox3 you have here. The definition of the word
User:Algentem/sandbox3 will help you to be more precise and correct when speaking or writing your texts. Knowing the definition of
User:Algentem/sandbox3, as well as those of other words, enriches your vocabulary and provides you with more and better linguistic resources.
...
The Coptic alphabet and transliteration
The Coptic alphabet have 31 characters derived from both the Greek alphabet and the Demotic cursive hieroglyphic script (marked in green). Unlike the original Greek alphabet, Coptic does not posses -a distinct upper case version of its letters.
Coptic does not have a set transliteration. But since it derived from the Greek alphabet, we can borrow the Greek transliteration with few changes.
| Case
|
Characters
|
| Upper
|
Ⲁ
|
Ⲃ
|
Ⲅ
|
Ⲇ
|
Ⲉ
|
Ⲍ
|
Ⲏ
|
Ⲑ
|
Ⲓ
|
Ⲕ
|
Ⲗ
|
Ⲙ
|
Ⲛ
|
Ⲝ
|
Ⲟ
|
Ⲡ
|
Ⲣ
|
Ⲥ
|
Ⲧ
|
Ⲩ
|
Ⲫ
|
Ⲭ
|
Ⲯ
|
Ⲱ
|
Ϣ
|
Ϥ
|
Ϧ
|
Ϩ
|
Ϫ
|
Ϭ
|
Ϯ
|
| Lower
|
ⲁ
|
ⲃ
|
ⲅ
|
ⲇ
|
ⲉ
|
ⲍ
|
ⲏ
|
ⲑ
|
ⲓ
|
ⲕ
|
ⲗ
|
ⲙ
|
ⲛ
|
ⲝ
|
ⲟ
|
ⲡ
|
ⲣ
|
ⲥ
|
ⲧ
|
ⲩ
|
ⲫ
|
ⲭ
|
ⲯ
|
ⲱ
|
ϣ
|
ϥ
|
ϧ
|
ϩ
|
ϫ
|
ϭ
|
ϯ
|
| Case
|
Transliteration
|
| Upper
|
A
|
B
|
G
|
D
|
E
|
Z
|
Ē
|
Th
|
I
|
K
|
L
|
M
|
N
|
Ks
|
O
|
P
|
R
|
S
|
T
|
U
|
Ph
|
Kh
|
Ps
|
Ō
|
Š
|
F
|
X
|
H
|
C
|
Ch
|
Ti
|
| Lower
|
a
|
b
|
g
|
d
|
e
|
z
|
ē
|
th
|
i
|
k
|
l
|
m
|
n
|
ks
|
o
|
p
|
r
|
s
|
t
|
u
|
ph
|
kh
|
ps
|
ō
|
š
|
f
|
x
|
h
|
c
|
ch
|
ti
|
Other letters
- Ϧ may be written either with a straight or a curled beginning.
- Akhmimic used its own Ⳉ (a modification of Ϩ /h/) instead of Ϧ /x/.
- Some earlier manuscripts contain a special adaption of shai "Ⳃ ⳃ" and a unique "Ⳋ ⳋ", both probably representing a voiceless palatal fricative (/ç/).
Origin
The origin for the additional seven characters — shai, fai, xai, hori, cancia, chima and tiei — is from Egyptian hieroglyphs through a mediate cursive form known as Demotic.
|
|
Characters
|
| Letter
|
Ϣ
|
Ϥ
|
Ϧ
|
Ϩ
|
Ϫ
|
Ϭ
|
Ϯ
|
| Hieroglyphic
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Demotic
|

|

|
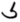
|

|

|

|

|
Vowels
All dialects seem to have had the same vowel set, but they utilized them differently.
Consonants
- ^ Absent in Bohairic.
- ^ Absent in Fayyumic, Lycopolitan, Oxyrhinchite, and Sahidic. Generally replaced by /h/.
Velar nasal
Scholars noticed a possible realization of a velar nasal, particularly in Sahidic. The digraph "ⲛⲕ" /nk/ may be interchanged with "ⲛⲅ" at the end of words. According to Vergote, Ernštedt, Loprieno and Kasser, this points to a realization of or , according to Hinze and Worrel , and according to Cartreau and Peust simply similar to German nk.
- ⲧⲱⲟⲩⲛⲅ (tōoung) “rise yourself” /ˈtownk/ or or from Egyptian dwn.k
The rare digraph "ⲙⲕ" /nk/ is also interchangeable with "ⲙⲅ". According to Peust, this is realized as :
- ⲟⲩⲱⲙⲅ (ouōmg) “to eat you” /ˈwomk/ from Egyptian wnm.k
Sahidic
Bohairic