父
| ||||||||
 | ||||||||
| ||||||||
Translingual
| Traditional | 父 |
|---|---|
| Simplified | 父 |
| Japanese | 父 |
| Korean | 父 |
| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|

| |||
Han character
父 (Kangxi radical 88, 父+0, 4 strokes, cangjie input 金大 (CK), four-corner 80400, composition ⿱八乂(GHJTV) or ⿱八⿻乀丿(K))
- Kangxi radical #88, ⽗.
Derived characters
- Appendix:Chinese radical/父
- 𠇑, 㕮, 𡵛, 㳇, 𣏤, 蚥, 𨊽, 䭸, 𫙉, 𩵹(𩽻), 𨚅, 𨾝, 𩾿
- 𠛈, 𫷁, 斧, 𭷕, 𤤎, 𤱇, 𧉊, 釜, 𬥐, 𨥏, 𮮕, 𫇫, 𢨰, 𠀱, 𤱀, 𩂎
References
- Kangxi Dictionary: page 690, character 1
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 19721
- Dae Jaweon: page 1103, character 1
- Hanyu Da Zidian (first edition): volume 3, page 2039, character 1
- Unihan data for U+7236
Further reading
Chinese
| simp. and trad. |
父 | |
|---|---|---|
| alternative forms | 𠇑 | |
Glyph origin
| Historical forms of the character 父 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shang | Western Zhou | Warring States | Shuowen Jiezi (compiled in Han) | Liushutong (compiled in Ming) |
| Oracle bone script | Bronze inscriptions | Chu slip and silk script | Small seal script | Transcribed ancient scripts |
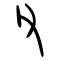
|

|

|
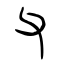
|
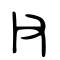
|
Pictogram (象形) – A hand holding a stone blade, referring to a man working with a stone axe.
Etymology
From Proto-Sino-Tibetan *paʔ (“male; father”).
Regular development from Middle Chinese would lead to the labiodental fù in Mandarin, but the colloquial word resisted the sound changes and is now written as 爸 (bà), with the 巴 (bā) phonetic component added to it to indicate the unchanged bilabial initial.
Pronunciation 1
- Mandarin
- Cantonese (Jyutping): fu6
- Gan (Wiktionary): fu5
- Hakka
- Northern Min (KCR): hū
- Eastern Min (BUC): hâu / hô
- Southern Min
- Wu (Northern, Wugniu): 6vu
- Xiang (Changsha, Wiktionary): fu4
- Mandarin
- (Standard Chinese)+
- Hanyu Pinyin: fù
- Zhuyin: ㄈㄨˋ
- Tongyong Pinyin: fù
- Wade–Giles: fu4
- Yale: fù
- Gwoyeu Romatzyh: fuh
- Palladius: фу (fu)
- Sinological IPA (key): /fu⁵¹/
- (Chengdu)
- Sichuanese Pinyin: fu4
- Scuanxua Ladinxua Xin Wenz: fu
- Sinological IPA (key): /fu²¹³/
- (Dungan)
- Cyrillic and Wiktionary: фу (fu, III)
- Sinological IPA (key): /fou⁴⁴/
- (Note: Dungan pronunciation is currently experimental and may be inaccurate.)
- (Standard Chinese)+
- Cantonese
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou–Hong Kong)
- Jyutping: fu6
- Yale: fuh
- Cantonese Pinyin: fu6
- Guangdong Romanization: fu6
- Sinological IPA (key): /fuː²²/
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou–Hong Kong)
- Gan
- (Nanchang)
- Wiktionary: fu5
- Sinological IPA (key): /fu¹¹/
- (Nanchang)
- Hakka
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Neipu)
- Pha̍k-fa-sṳ: fu
- Hakka Romanization System: fu
- Hagfa Pinyim: fu4
- Sinological IPA: /fu⁵⁵/
- (Hailu, incl. Zhudong)
- Hakka Romanization System: fuˇ
- Sinological IPA: /fu¹¹/
- (Meixian)
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Neipu)
- Northern Min
- (Jian'ou)
- Kienning Colloquial Romanized: hū
- Sinological IPA (key): /xu⁵⁵/
- (Jian'ou)
- Eastern Min
- (Fuzhou)
- Bàng-uâ-cê: hâu / hô
- Sinological IPA (key): /hɑu²⁴²/, /hou²⁴²/
- (Fuzhou)
- Southern Min
- hu6 - literary;
- bê6 - semantic (original character is 爸).
- Middle Chinese: bjuX
- Old Chinese
- (Baxter–Sagart): /*(r)aʔ/
- (Zhengzhang): /*baʔ/
Definitions
父
- father (male parent)
- 父親/父亲 ― fùqīn ― (formal) father
- 父母 ― fùmǔ ― parents; father and mother
- 父子 ― fùzǐ ― father and son
- 父女 ― fùnǚ ― father and daughter
- 父輩/父辈 ― fùbèi ― one's father's generation
- 家父 ― jiāfù ― (humble) my father
- 生父 ― shēngfù ― biological father
- 養父/养父 ― yǎngfù ― adoptive father
- 繼父/继父 ― jìfù ― stepfather
- Antonym: 母 (mǔ)
- Used to address a male elder member of a family.
- 祖父 ― zǔfù ― paternal grandfather (one's father's father)
- 伯父 ― bófù ― paternal uncle (father's elder brother)
- 叔父 ― shūfù ― paternal uncle (father's younger brother)
- 岳父 ― yuèfù ― father-in-law (wife's father)
- 舅父 ― jiùfù ― maternal uncle (mother's brother)
- 姨父 ― yífù ― maternal uncle (husband of mother's sister)
- 姑父 ― gūfù ― paternal uncle (husband of father's sister)
- Antonym: 母 (mǔ)
- father (pioneering male figure in a particular field)
- 雜交水稻之父/杂交水稻之父 ― zájiāo shuǐdào zhī fù ― (specifically) Father of Hybrid Rice (Yuan Longping)
- 國父/国父 ― guófù ― father of a nation; (specifically) Father of the Republic (Sun Yat-sen)
- (Christianity) Father; God the Father
- 天父 ― Tiānfù ― Heavenly Father
Synonyms
Pronunciation 2
- Mandarin
- (Standard Chinese)+
- Hanyu Pinyin: fǔ
- Zhuyin: ㄈㄨˇ
- Tongyong Pinyin: fǔ
- Wade–Giles: fu3
- Yale: fǔ
- Gwoyeu Romatzyh: fuu
- Palladius: фу (fu)
- Sinological IPA (key): /fu²¹⁴/
- (Standard Chinese)+
- Cantonese
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou–Hong Kong)
- Jyutping: fu2
- Yale: fú
- Cantonese Pinyin: fu2
- Guangdong Romanization: fu2
- Sinological IPA (key): /fuː³⁵/
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou–Hong Kong)
- Southern Min
- (Hokkien: Xiamen)
- Pe̍h-ōe-jī: hú
- Tâi-lô: hú
- Phofsit Daibuun: huo
- IPA (Xiamen): /hu⁵³/
- (Teochew)
- Peng'im: hu6 / hu2
- Pe̍h-ōe-jī-like: hŭ / hú
- Sinological IPA (key): /hu³⁵/, /hu⁵²/
- (Hokkien: Xiamen)
- Middle Chinese: pjuX
- Old Chinese
- (Baxter–Sagart): /*p(r)aʔ/
- (Zhengzhang): /*paʔ/
Definitions
父
- (literary, respectful) old man; elderly man
- (literary) alternative form of 甫 (“honorific suffix used after a man's name; courtesy name”)
- a surname
Compounds
- 一過不父 / 一过不父
- 丁父憂 / 丁父忧 (dīngfùyōu)
- 丁父艱 / 丁父艰
- 三父八母
- 世父 (shìfù)
- 中父
- 主父
- 乃父
- 五父
- 亞父 / 亚父
- 亡父 (wángfù)
- 亭父
- 亶父
- 人父 (rénfù)
- 任父
- 仲父
- 伯夷父
- 伯父 (bófù)
- 俗父
- 假父
- 傅年父母
- 傅父 (fùfù)
- 傖父 / 伧父 (cāngfǔ)
- 儈父 / 侩父
- 元父
- 先父 (xiānfù)
- 兒無常父 / 儿无常父
- 內父 / 内父
- 公父
- 公父訓 / 公父训
- 公祖父母
- 再從父 / 再从父
- 再生父母 (zàishēng fùmǔ)
- 冶父
- 力父
- 十阿父
- 博父國 / 博父国
- 叔父 (shūfù)
- 古公亶父
- 召父杜母
- 名父
- 同父
- 君山老父
- 君師父 / 君师父
- 君父 (jūnfù)
- 單父 / 单父
- 單父琴 / 单父琴
- 嗣父母
- 嘯父 / 啸父
- 嚴父 / 严父 (yánfù)
- 國父 / 国父 (guófù)
- 土父
- 圻父
- 壤父
- 外大父
- 外父 (wàifù)
- 外王父
- 外祖父 (wàizǔfù)
- 大師父 / 大师父
- 大父 (dàfù)
- 大王父
- 太父
- 天父 (tiānfù)
- 夸父
- 夸父追日
- 夸父逐日
- 契父 (qìfù)
- 姑父
- 姨父
- 嫡父
- 子州支父
- 子承父業 / 子承父业 (zǐchéngfùyè)
- 子為父隱 / 子为父隐
- 子父
- 孔宣父
- 孔父
- 孔父嘉
- 季父 (jìfù)
- 宏父
- 宗父
- 宣父
- 家人父子
- 宰父 (Zǎifù)
- 家父 (jiāfù)
- 寄父 (jìfù)
- 富父
- 封父
- 射父
- 小父
- 尚父 (shàngfù)
- 尼父
- 山父
- 岳父 (yuèfù)
- 巢父
- 師尚父 / 师尚父
- 師父 / 师父 (shīfu)
- 師父娘 / 师父娘
- 幹父 / 干父
- 幹父之蠱 / 干父之蛊
- 弒父 / 弑父 (shìfù)
- 弓父
- 弟父
- 後父 / 后父 (hòufù)
- 徒父
- 從父 / 从父
- 從父兄 / 从父兄
- 從父姊妹 / 从父姊妹
- 從祖父 / 从祖父
- 從祖祖父 / 从祖祖父
- 恩同父母
- 愚父
- 慈父 (cífù)
- 慶父 / 庆父
- 戀父情結 / 恋父情结
- 支父
- 教父 (jiàofù)
- 教父哲學 / 教父哲学
- 斫父
- 族曾王父
- 族曾祖父
- 族父
- 族父母
- 族祖父
- 族祖父母
- 是父是子
- 晚父
- 曾大父
- 曾父
- 曾王父
- 曾祖父 (zēngzǔfù)
- 曾祖王父
- 有其父必有其子 (yǒu qí fù bì yǒu qí zǐ)
- 朴父
- 杖父
- 村父
- 村父老
- 杜父魚 / 杜父鱼 (dùfùyú)
- 東父 / 东父
- 東王父 / 东王父
- 柏亮父
- 柏夷亮父
- 桂父
- 梁父
- 梁父吟
- 梁父山 (Liángfǔshān)
- 樵父
- 樸父 / 朴父
- 正父
- 江東父老 / 江东父老
- 漁父 / 渔父 (yúfǔ)
- 漁父引 / 渔父引
- 漁父曲 / 渔父曲
- 漁父行 / 渔父行
- 漢陰老父 / 汉阴老父
- 無父 / 无父
- 無父無君 / 无父无君
- 父世縣 / 父世县
- 父事
- 父任
- 父債子還 / 父债子还 (fùzhàizǐhuán)
- 父兄 (fùxiōng)
- 父喪 / 父丧
- 父嚴子孝 / 父严子孝
- 父國 / 父国
- 父執 / 父执 (fùzhí)
- 父執輩 / 父执辈
- 父天
- 父天母地
- 父子 (fùzǐ)
- 父子兵
- 父子同牝
- 父子天性
- 父子軍 / 父子军
- 父宗
- 父師 / 父师
- 父息
- 父慈子孝 (fùcízǐxiào)
- 父憂 / 父忧
- 父族
- 父服
- 父析子荷
- 父業 / 父业 (fùyè)
- 父權 / 父权 (fùquán)
- 父母 (fùmǔ)
- 父母之命
- 父母之邦
- 父母國 / 父母国
- 父母子女
- 父母官 (fùmǔguān)
- 父母恩勤
- 父母雙亡 / 父母双亡
- 父母骨肉
- 父為子隱 / 父为子隐
- 父王 (fùwáng)
- 父祖 (fùzǔ)
- 父禰 / 父祢
- 父精母血
- 父系 (fùxì)
- 父系制度
- 父老 (fùlǎo)
- 父臺 / 父台
- 父舅
- 父艱 / 父艰
- 父蔭 / 父荫
- 父親 / 父亲 (fùqīn)
- 父親節 / 父亲节 (fùqīnjié)
- 父賞 / 父赏
- 父輩 / 父辈 (fùbèi)
- 父道
- 父馬 / 父马
- 父黨 / 父党
- 狐父
- 猶父 / 犹父
- 猿父
- 王大父
- 王父
- 生父 (shēngfù)
- 田父 (tiánfù)
- 甲父
- 田父之功
- 田父之獲 / 田父之获
- 田父野叟
- 田父野老
- 異父 / 异父
- 皇父
- 相父
- 眾父 / 众父
- 眾父父 / 众父父
- 瞿父
- 祈父
- 神父 (shénfù)
- 祖父 (zǔfù)
- 祖父母 (zǔfùmǔ)
- 祖王父
- 穀父蠶母 / 谷父蚕母
- 粉父
- 緹縈救父 / 缇萦救父
- 縣父母 / 县父母
- 繼父 / 继父 (jìfù)
- 罕父
- 義父 / 义父 (yìfù)
- 老師父 / 老师父
- 老父 (lǎofù)
- 老父母
- 老父臺 / 老父台 (lǎofùtái)
- 耕父
- 聖父 / 圣父 (Shèngfù)
- 肉父
- 舅父 (jiùfù)
- 舉父 / 举父
- 苗父
- 虜父 / 虏父
- 蚚父
- 蜜父
- 衣食父母 (yīshífùmǔ)
- 親生父母 / 亲生父母
- 言父
- 許父 / 许父
- 認仇作父 / 认仇作父
- 認敵作父 / 认敌作父
- 認賊作父 / 认贼作父 (rènzéizuòfù)
- 認賊為父 / 认贼为父
- 誼父 / 谊父
- 諸父 / 诸父
- 證父 / 证父
- 證父攘羊 / 证父攘羊
- 谿父
- 豪父
- 貜父
- 資父 / 资父
- 賣身葬父 / 卖身葬父
- 越石父
- 跨牛父
- 農父 / 农父
- 造父
- 那父
- 邵父
- 郊父
- 重生父母 (chóngshēng fùmǔ)
- 野父
- 門父 / 门父
- 阿父 (āfù)
- 雄父
- 雍父
- 電父 / 电父
- 章父
- 章父薦屨 / 章父荐屦
- 頑父嚚母 / 顽父嚚母
- 顯父 / 显父
- 養不教,父之過 / 养不教,父之过 (yǎngbùjiào, fùzhīguò)
- 養父 / 养父 (yǎngfù)
- 養身父母 / 养身父母
- 高祖父 (gāozǔfù)
- 高祖王父
- 魁父
- 魚父 / 鱼父
- 麝父
- 麟父筆 / 麟父笔
- 黃父 / 黄父
- 黃父鬼 / 黄父鬼
References
- “父”, in 漢語多功能字庫 (Multi-function Chinese Character Database), 香港中文大學 (the Chinese University of Hong Kong), 2014–
- Dictionary of Chinese Character Variants (教育部異體字字典), A02471
- Ding, Fubao (丁福保) (1922),
 “父” in 佛學大辭典 .
“父” in 佛學大辭典 .
Japanese
| Shinjitai | 父 | 
|
| Kyūjitai | 父󠄁 父+ 󠄁?(Adobe-Japan1) |

|
| The displayed kanji may be different from the image due to your environment. See here for details. | ||
Kanji
Readings
- Go-on: ぶ (bu)、ふ (fu, Jōyō)
- Kan-on: ふ (fu, Jōyō)
- Kan’yō-on: ほ (ho)
- Kun: ちち (chichi, 父, Jōyō)、てて (tete, 父)、とと (toto, 父)、ちゃん (chan, 父)、かそ (kaso, 父)
- Nanori: のり (nori)
Compounds
Etymology 1
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 父 |
| ちち Grade: 2 |
| kun'yomi |
From Old Japanese 父 (titi), from Proto-Japonic *titi.
Still in modern usage.
Pronunciation
- (Tokyo) ちち (Atamadaka – )
- (Tokyo) ちち (Odaka – ) non-lexical pitch that some speakers employ to reconcile coinciding devoicing and accenting
- IPA(key):
Noun
- father
- 野比のび助は、主人公のび太の父。
- Nobi Nobisuke wa, shujinkō Nobita no chichi.
- Nobi Nobisuke is the father of the protagonist Nobita.
- 938, Minamoto no Shitagō, Wamyō Ruijushō, volume 1, page 115:
- 父 爲考、和名知々、日本紀私記云加曾
- chichi sukō, wamei chichi, Nihon Ki Shiki iu kaso
- Father: considered in Japanese as chichi; in the Nihon Shoki Shiki it is pronounced kaso
- 父 爲考、和名知々、日本紀私記云加曾
- 野比のび助は、主人公のび太の父。
- (by extension, figurative) a father figure (male initiator or founder of something)
- (Christianity) God, the Holy Father
Usage notes
- This term conveys neither positive nor negative connotations. However, using it to describe someone the speaker knows personally is often considered lacking respect, where more polite forms like お父さん (otōsan) are preferred.
- This term is sometimes used in objective narrations, but for this purpose, 父親 (chichioya) is more common.
Antonyms
Derived terms
- 父君 (chichigimi)
- 父御 (chichigo)
- 父者人 (chichija hito)
- 小父 (oji)
- 伯父 (oji)
- 叔父 (oji)
- 親父 (oyaji)
- 父上 (chichiue, “honourable father”, term in respect primarily used in writing)
- 父親 (chichioya, “father”, specifically as someone's parent)
- 父無し子 (chichinashigo, “fatherless child”)
- 父母 (chichihaha, “father and mother, both parents”)
Etymology 2
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 父 |
| てて Grade: 2 |
| kun'yomi |
Appears in the Utsubo Monogatari of roughly 970 CE.
Glossed as “I, chichi. Pay” (“same as chichi. Father”) in Nippo Jisho.
Usage continued until at least the early 1700s.
Pronunciation
Noun
Derived terms
Etymology 3
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 父 |
| とと Grade: 2 |
| kun'yomi |
Appears in the Nippo Jisho of 1603.
Originally a shift from chichi or tete in baby talk, used by children to refer to their own father.
Still in modern usage.
Pronunciation
Noun
- (childish) one's own father: daddy
- Coordinate term: 母 (kaka)
- (by later extension) a husband, master of the house
Derived terms
Etymology 4
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 父 |
| ちゃん Grade: 2 |
| kun'yomi |
| Alternative spelling |
|---|
| 爺 |
/totosan/ → /totːɕan/ → /t͡ɕan/
Likely a contraction of 父さん (toto-san).
Pronunciation
Noun
- (informal, possibly dialect) one's own father
- (by later extension) the head or master of an establishment such as a teahouse, boathouse, etc.
Etymology 5
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 父 |
| ふ Grade: 2 |
| goon |
The “father” and “uncle” affixes is from Middle Chinese 父 (MC bjuX).
The “old man” affix is from Middle Chinese 父 (MC pjuX).
Pronunciation
Affix
Derived terms
Etymology 6
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 父 |
| ほ Grade: 2 |
| kan'yōon |
From a corruption of Middle Chinese 父 (MC pjuX).
Pronunciation
Affix
Derived terms
- 尼父 (Jiho)
Etymology 7
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 父 |
| かそ Grade: 2 |
| kun'yomi |
⟨kaso2⟩ → */kasə/ → /kaso/ → /kazo/
From Old Japanese. Appears in the Nihon Shoki of 720 CE as unvoiced kaso. Further derivation unknown.
May have fallen out of use by 1603, when neither kaso nor kazo are found in the Nippo Jisho. Kaso would be here as the sixth entry from the bottom on the left, and kazo would be here as the eighth from the bottom on the right.
Pronunciation
Noun
- (obsolete) one's own father
- 938, Minamoto no Shitagō, Wamyō Ruijushō, volume 1, page 115:
- 父 爲考、和名知々、日本紀私記云加曾
- chichi sukō, wamei chichi, Nihon Ki Shiki iu kaso
- Father: considered in Japanese as chichi; in the Nihon Shoki Shiki it is pronounced kaso
- 父 爲考、和名知々、日本紀私記云加曾
Derived terms
- 父母 (kazo iroha)
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Matsumura, Akira, editor (2006), 大辞林 (in Japanese), Third edition, Tokyo: Sanseidō, →ISBN
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 NHK Broadcasting Culture Research Institute, editor (1998), NHK日本語発音アクセント辞典 (in Japanese), Tokyo: NHK Publishing, Inc., →ISBN
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 Shōgaku Tosho (1988) 国語大辞典(新装版) (in Japanese), Tōkyō: Shogakukan, →ISBN
- ^ “Tete”, in Nippo Jisho, 1604, page 256
- ^ Matsumura, Akira, editor (1995), 大辞泉 (in Japanese), First edition, Tokyo: Shogakukan, →ISBN
- ^ Kindaichi, Kyōsuke et al., editors (1997), 新明解国語辞典 (in Japanese), Fifth edition, Tokyo: Sanseidō, →ISBN
Korean
Etymology 1
From Middle Chinese 父 (MC bjuX, “father”).
- Recorded as Middle Korean 뿡〯 (Yale: ppwǔ?) in Dongguk Jeongun (東國正韻 / 동국정운), 1448.
- Recorded as Middle Korean 부〮 (pwú)訓 (Yale: pwú) in Hunmong Jahoe (訓蒙字會 / 훈몽자회), 1527.
- Recorded as Middle Korean 부 ( pwu)訓 (Yale: pwu) in Gwangju Cheonjamun (光州千字文 / 광주천자문), 1575.
- Recorded as Middle Korean 부 ( pwu)訓 (Yale: pwu) in Sinjeung Yuhap (新增類合 / 신증유합), 1576.
Pronunciation
- (SK Standard/Seoul) IPA(key):
- Phonetic hangul:
Hanja
Compounds
- 부계 (父系, bugye)
- 부권 (父權, bugwon)
- 부녀 (父女, bunyeo)
- 부도 (父道, budo)
- 부로 (父老, buro)
- 부명 (父命, bumyeong)
- 부모 (父母, bumo)
- 부사 (父師, busa)
- 부자 (父子, buja)
- 부조 (父祖, bujo)
- 부집 (父執, bujip)
- 부친 (父親, buchin)
- 부형 (父兄, buhyeong)
- 가부 (家父, gabu)
- 계부 (繼父, gyebu)
- 군부 (君父, gunbu)
- 내부 (乃父, naebu)
- 노부/로부 (老父, nobu/robu)
- 대부 (代父, daebu)
- 망부 (亡父, mangbu)
- 백부 (伯父, baekbu)
- 빙부 (聘父, bingbu)
- 사부 (師父, sabu)
- 생부 (生父, saengbu)
- 성부 (聖父, seongbu)
- 숙부 (叔父, sukbu)
- 신부 (神父, sinbu)
- 악부 (岳父, akbu)
- 양부 (養父, yangbu)
- 어부 (漁父, eobu)
- 엄부 (嚴父, eombu)
- 왕부 (王父, wangbu)
- 유부 (猶父, yubu)
- 의부 (義父, uibu)
- 이부 (李父, ibu)
- 자부 (慈父, jabu)
- 제부 (諸父, jebu)
- 조부 (祖父, jobu)
- 천부 (天父, cheonbu)
- 친부 (親父, chinbu)
- 부사지 (父事之, busaji)
- 부선망 (父先亡, buseonmang)
- 부주전 (父主前, bujujeon)
- 조부모 (祖父母, jobumo)
- 고조부 (高祖父, gojobu)
- 족대부 (族大父, jokdaebu)
- 족조부 (族祖父, jokjobu)
- 증조부 (曾祖父, jeungjobu)
Etymology 2
From Middle Chinese 父 (MC pjuX, “old man; elderly man”).
- Recorded as Middle Korean 붕〯 (Yale: pwǔ?) in Dongguk Jeongun (東國正韻 / 동국정운), 1448.
Pronunciation
- (SK Standard/Seoul) IPA(key):
- Phonetic hangul:
Hanja
Compounds
References
Old Japanese
Etymology 1
Reduplication of ti below.
Noun
父 (titi) (kana ちち)
- one's own father
- Coordinate term: 母 (omo, papa)
- , text here
- ...奥床仁母者睡有外床丹父者寐有...
- ...okuto2ko2 ni papa pa inetari to1do2ko2 ni titi pa inetari...
- (please add an English translation of this usage example)
Derived terms
Descendants
- Japanese: 父 (chichi, tete, toto)
Etymology 2
Eastern dialect of titi above.
Noun
父 (sisi) (kana しし)
Derived terms
Etymology 3
From Proto-Japonic *ti.
Noun
父 (ti) (kana ち)
- (honorific) a term of respect for males
- 711–712, Kojiki, poem 48:
- 加志能布邇余久須袁都久理余久須邇迦美斯意富美岐宇麻良爾岐許志母知袁勢麻呂賀知
- kasi no2 pu ni yo2kusu wo tukuri yo2kusu ni kami1si opomi1ki1 umara ni ki1ko2simo2tiwose maro2 ga ti
- (please add an English translation of this usage example)
- Note: Poem 39 of the Nihon Shoki is similar to this but replaces 迦美斯 (kami1si) with 伽綿蘆 (kame1ru).
Derived terms
Etymology 4
Noun
父 (kaso2) (kana かそ)
- one's own father
- Antonym: 母 (iro2pa)
- 720, Nihon Shoki, Emperor Ninken, entry 11: sixth year, ninth month in autumn:
- 菱城邑人鹿父〈鹿父、人名也。俗、呼父為柯曾〉聞而向前曰「何哭之哀甚、若此乎」。
- A man of Pisikï village, Kakasö (his name is Kakasö; it was customary to call one's father kasö) heard cries, turned to her, and asked, “Why these cries of grief, young one?”
Descendants
- Japanese: 父 (kazo)
References
- ^ Matsumura, Akira, editor (2006), 大辞林 (in Japanese), Third edition, Tokyo: Sanseidō, →ISBN
- ^ Shōgaku Tosho (1988) 国語大辞典(新装版) (in Japanese), Tōkyō: Shogakukan, →ISBN
Vietnamese
Han character
父: Hán Việt readings: phụ (
父: Nôm readings: phụ, phủ
Affix
父 (phụ)

